The world runs on connectivity. Whenever someone taps their phone to stream, pay, or simply scroll, they trigger a chain reaction across a highly complex telecom infrastructure that processes, tracks, and bills their usage in real time. Behind these seemingly instant transactions lies a sophisticated ecosystem of telecom billing software.
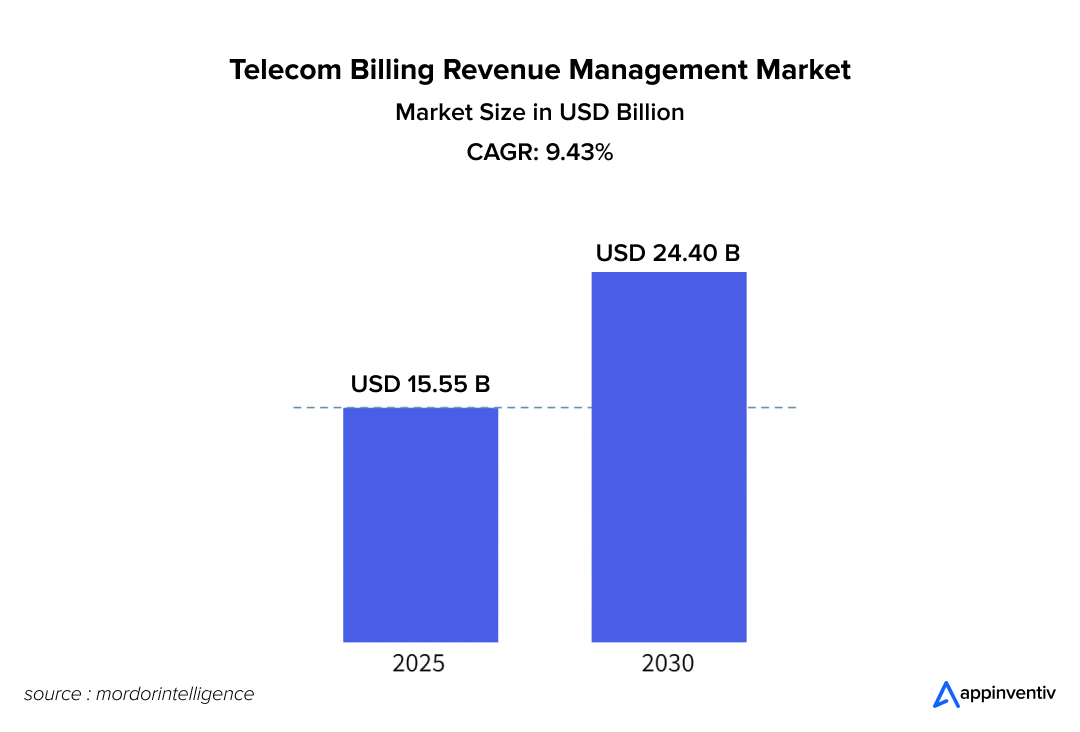
The Telecom Billing and Revenue Management Market is projected to grow significantly over the next few years. It is estimated to be valued at USD 15.55 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 24.40 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.43%. (Source: Mordor Intelligence)
It’s 2025, and telecom billing and software solutions are no longer just tracking usage and generating invoices. They’re about integrating diverse services, managing complex pricing models, managing partnerships, and improving customer transparency.
With this growing market, telecom businesses navigate an environment shaped by 5G, IoT, and on-demand digital experiences. Yet, many telecom operators still rely on outdated, fragmented systems. But how to build custom telecom billing and software solutions which are not only capable of handling today’s challenges but also prepared for the demands of tomorrow’s 5 G-powered, IoT-enabled world?
Here is a complete breakdown of telecom billing software development, including the process, cost, features, benefits, and more!
So, let’s start by understanding the telecom billing system.
Understanding Telecom Billing System
To understand the billing system in telecom software, let’s take a look at the typical user flow of a telecom billing software with an example:
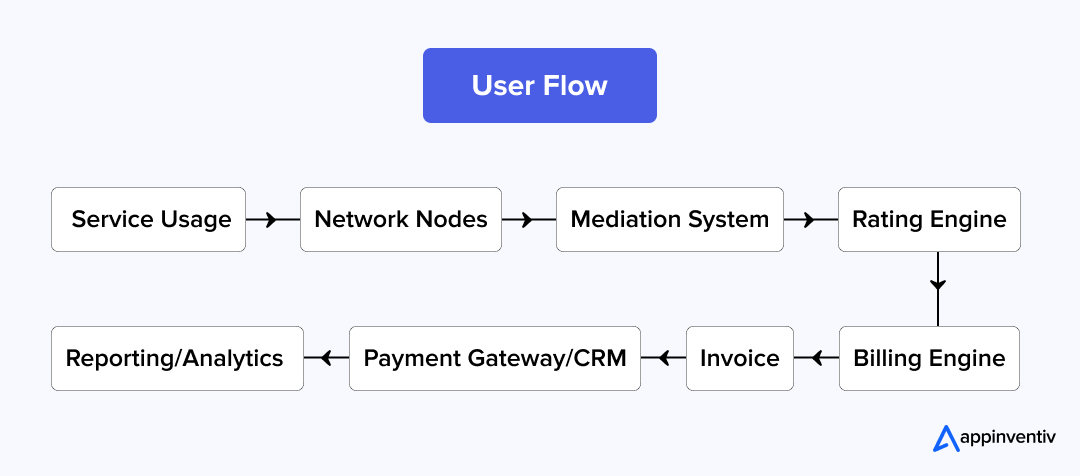
Example for a mobile data session:
- Users consume services like calling, using data, or sending an SMS.
- The network nodes capture the usage data (e.g., call data records or session logs).
- The data is normalized and forwarded to the billing system.
- The system applies the appropriate pricing rules (e.g., ₹0.02 per MB of data or ₹0.05 per minute of call).
- The system generates an invoice or deducts the usage cost from the prepaid balance.
- For postpaid users, a bill is created at the end of the billing cycle, or real-time deductions are made for prepaid users.
- The user pays via credit card, mobile wallet, or prepaid balance top-up.
- The system generates reports and tracks financial performance, usage patterns, and customer behavior.
The advanced telecom billing platforms are built on a well-structured architecture composed of several interconnected components to handle such diversity.
Telecom Billing System Architecture
The architecture explains how telecom billing systems work:
| Component |
Functionality |
| Mediation Engine |
Collects raw usage data from network elements and standardizes it for further processing. |
| Rating & Charging Engine |
Applies rating logic to calculate the charges for different services (calls, SMS, data, etc.) based on usage. |
| Billing Engine |
Generates invoices, applies charges, and manages different billing cycles, including discounts and tax calculations. |
| CRM Integration |
Manages customer data, including account information, service plans, preferences, and subscription lifecycle. |
| Payment Gateway Integration |
Handles payment processing, including digital transactions (credit cards, wallets), refunds, and auto-recharges. |
| Reporting & Analytics |
Provides insights through reporting dashboards on KPIs such as ARPU, churn rate, usage patterns, and SLA compliance. |
Types of Billing in the Telecom Industry
The billing cycle determines the core logic of your billing system in telecom software, from how usage is rated to how revenue is collected, and how scalable your offering can be across markets. Here are three types of billing in the telecom industry that shape how the billing system in telecom software works:
Prepaid Billing:
Customers pay upfront and are charged in real time for every second, byte, or message used.
- A telecom charging system (OCS) deducts balance instantly as users consume services.
- Session cutoffs and balance alerts occur in real time.
- Periodic statements can be issued, though payment is made in advance.
Ideal for prepaid mobile plans, IoT/M2M connectivity, and digital-first telcos.
Postpaid Billing:
Customers use services first and are billed at the end of a predefined cycle, usually 30, 45, or 60 days.
- Service usage is collected via mediation systems and processed by the rating engine.
- The billing system generates a consolidated invoice, including taxes, surcharges, and optional add-ons.
- Customers typically pay after the invoice is received.
Ideal for enterprise telecom accounts, high-value customers, and contract-based telecom services.
Convergent Billing:
Combines prepaid and postpaid services and voice, data, broadband, IPTV, and IoT into a single bill across accounts, users, or products.
- The billing engine merges data from multiple systems and applies common usage and charges per account.
- Users see one invoice that includes all services and charges.
This is ideal for telcos offering multiple services (mobile + broadband + TV + IoT), 5G monetization, family sharing, and hybrid plans.
Benefits of Telecom Billing Systems
Now that we have understood how telecom billing solutions work, let’s see how you can benefit from them!
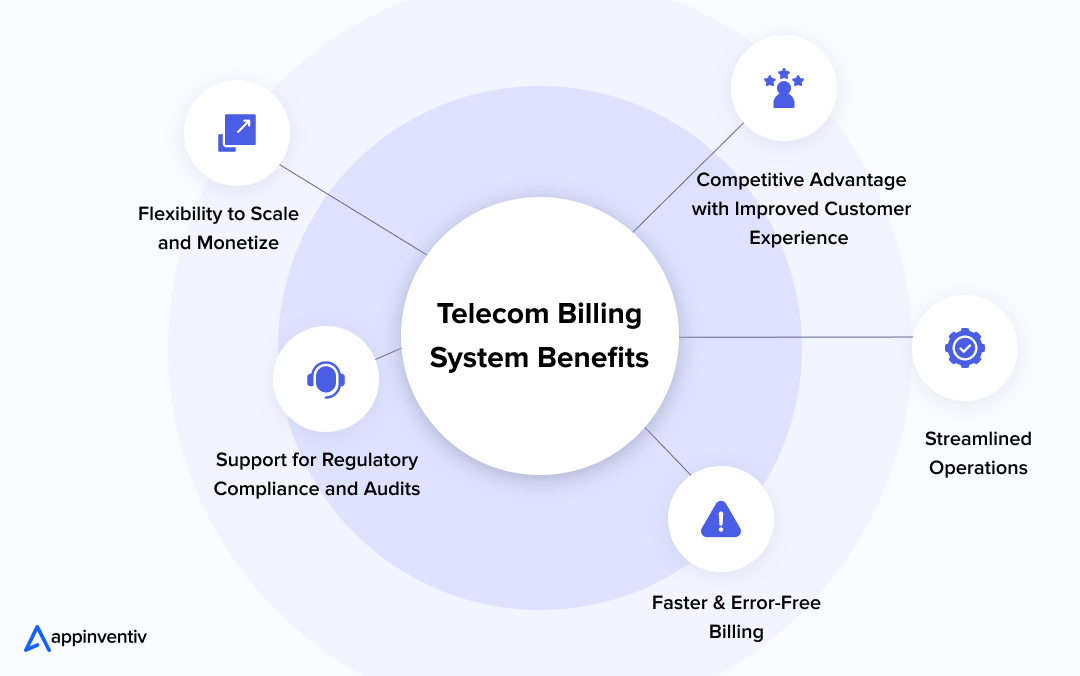 Faster & Error-Free Billing
Faster & Error-Free Billing
A telecom billing system automates every aspect of the billing lifecycle from usage tracking and rating to invoice generation, ensuring accuracy and speed. It reduces billing errors, speeds up billing cycles, and improves customer trust.
Streamlined Operations
A centralized billing system eliminates the need for fragmented tools, repetitive manual work, and excessive admin hours. Standardizing workflows brings all your billing into one streamlined workflow, whether prepaid, postpaid, or converged. This means fewer admin hours, fewer errors, and lower staffing costs.
Flexibility to Scale and Monetize
Whether you’re launching a new IoT service, combining broadband with OTT, or managing complex enterprise plans, a telecom billing system allows seamless adaptation without rebuilding infrastructure. It helps you bring new offers to market faster, customize pricing for various customer segments, and run global operations smoothly, all from a single platform.
Support for Regulatory Compliance and Audits
You must handle strict rules regarding data privacy, taxes, customer verification, and digital transactions. A SaaS telecom billing solution takes care of these requirements in the background. It automatically applies taxes, handles regional charges, and keeps detailed records of every transaction. This saves time and lowers the risk of mistakes, penalties, or legal trouble during audits.
Competitive Advantage with Improved Customer Experience
Today’s users expect everything, plans, bills, payments, and support, to be digital, instant, and seamless. Billing software helps you meet these expectations by enabling real-time interactions and 24/7 chat support. It also makes launching special offers, loyalty rewards, or flexible plans based on customer needs easier, helping you stay competitive and customer-focused.
Telecom Billing and Software Solutions: Must-Have Features
The features embedded in your billing system determine its scalability, agility, and monetizing ability. So, here are some core features that you must include to automate operations, ensure billing accuracy, and deliver a seamless customer experience:

Usage Data Collection & Mediation
This feature collects usage data from different network systems, such as calls, messages, and internet usage, and converts it into a single, consistent format. It helps ensure the data is clean, complete, and ready for billing. Without this step, there’s a risk of duplicate records, missing data, or mismatches, which can cause billing mistakes and lost revenue.
Example: You use mediation to collect call records from both 4G and VoIP networks. These records are filtered, de-duplicated, and converted into a standard format before being passed to the rating engine, ensuring accurate billing across all service types.
Rating and Charging Engine
This engine determines how much to charge users based on how they use services, their plans, and any discounts or offers applied. It handles complex pricing in real time or batches, and works for prepaid, postpaid, or hybrid models. Getting this right is critical as it directly impacts customers’ bills and business revenue.
Example: When a user streams video on a weekend under a special promo plan, the rating engine calculates the discount in real time and updates the charge accordingly, ensuring accurate and fair billing without manual adjustments.
Invoice Generation
This feature automatically compiles usage data, applies taxes, fees, and discounts, and generates clear, itemized invoices for each customer. Timely and transparent invoicing improves customer trust while helping telecoms speed up their billing cycles.
Example: A telecom company schedules monthly invoicing, and the billing system auto-generates bills for all postpaid users with complete details like call duration, data used, and applicable taxes sent via email or app notifications.
NOTE: Rating and invoicing might be confusing.
Rating = How much each service costs, and
Invoicing = Creating the final bill with all charges included.
Account & Customer Management
Telecom billing software provides a unified view of customer accounts, including their plans, payments, balances, and history. It allows support teams to manage upgrades, suspensions, and service changes from a single dashboard, improving operational efficiency and customer experience.
Example: When a customer upgrades to a new plan mid-cycle, the billing system automatically calculates and reflects the adjusted charges in the next invoice.
Payment Gateway Integration
The system must integrate with various payment gateways to support digital transactions via cards, wallets, UPI, or net banking. This enables an automated, secure, and flexible payment process.
Example: A user receives their e-bill through the mobile app and pays instantly via Google Pay. The system updates the payment status and sends a receipt, improving convenience and reducing DSO (Days Sales Outstanding).
Taxation and Compliance Management
Tax compliance software development solution ensures compliance with local, national, and international telecom regulations. It automates tax calculation, handles region-based surcharges, and keeps detailed records that make audits and financial reviews easier.
Example: A telecom firm operating in multiple states applies different VAT and telecom levies per region. The billing software calculates and adds these charges to the invoice, eliminating manual errors and regulatory risks.
Reporting and Analytics
Built-in reporting and analytics give you a clear view of your business, from daily revenue and service usage to churn patterns and customer preferences. With real-time dashboards and historical data, teams can spot trends, track performance, and use business intelligence make data-driven decisions around pricing, resource allocation, and customer engagement strategies.
Example: A monthly report shows a spike in video data usage among metro area subscribers. Based on this, you can launch a new streaming-focused data pack and target it to the right customer segment.
Plan and Offer Management
You can create, launch, and manage new service plans and promotions with minimal technical effort. The feature allows marketing teams to experiment with pricing strategies while keeping billing systems current.
Example: You run a seasonal promotion offering 5% extra data on specific plans. The billing software applies the offer automatically and reverts to normal pricing when the campaign ends.
Futuristic AI-Powered Features
While the core features of telecom billing software are essential for day-to-day operations, looking ahead to future requirements is just as important for long-term success. So, here are some future-ready or AI-powered features that you can consider:
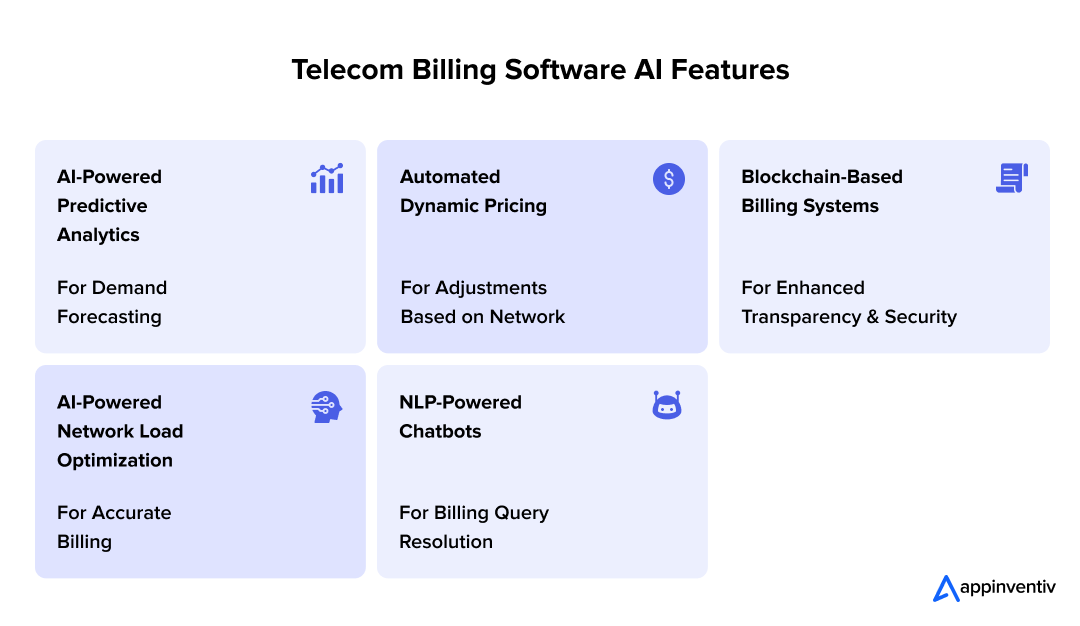
AI-Powered Predictive Analytics for Demand Forecasting
Predicting customer behavior and network usage can make you stay ahead of the game in a data-driven world. AI can mine large datasets to identify patterns in customer usage, peak demand periods, and emerging trends.
Automated Dynamic Pricing Based on Network Conditions
As customer expectations shift towards more flexible service offerings, dynamic pricing will become a game-changer. AI will help you implement real-time dynamic pricing, adjusting charges based on network congestion, data usage, and even geographical location.
Blockchain-Based Billing Systems for Enhanced Transparency and Security
As telecom companies handle more digital transactions, fraud prevention and transparency can be big concerns. Since blockchain is decentralized, it ensures that the data is reliable and can’t be altered, making it easier for telecom providers to keep accurate billing records.
AI-Powered Network Load Optimization for Accurate Billing
AI in the telecom industry can predict network load fluctuations based on real-time traffic patterns, enabling telecom providers to optimize network resources.
NLP-Powered Chatbots for Billing Query Resolution
These AI-driven chatbots can understand and respond to customer inquiries in natural language, offering support for various billing-related issues, from explaining charges to resolving disputes. Available 24/7, these chatbots can instantly provide accurate, real-time answers.
Telecom Billing Software Development Process
By now, you would know that building a telecom billing system goes far beyond coding! It’s about architecting a solution that scales, stays compliant, and monetizes services efficiently. Here’s a complete, step-by-step breakdown:
Requirement Gathering and Business Analysis
Before getting into telecom billing software development, the first step is to conduct a comprehensive business analysis to gather all necessary requirements. Also, define the foundation of your telecom billing software.
How can you do this? Start by talking to operators, finance teams, customer support, and tech teams to identify operational gaps in current billing systems, customer segments, and compliance expectations.
Document service types (prepaid/postpaid/hybrid), geographies covered, monetization models, integration needs, and KPIs like ARPU, churn rate, or time-to-bill.
Expert Tip: Involve all departments early on, from marketing to legal, as this will help align the technical or legal requirements (like GDPR Compliant Software, TRAI, or FCC) with business objectives that could impact design later.
Define the Telecom Billing System Architecture
Once you have identified the business needs, the next step is to architect the solution. This includes defining how different modules interact, like the mediation system, rating engine, invoice engine, payment orchestration platform, CRM, and OSS/BSS layers.
The architecture must support high-volume usage data processing, modular growth, microservices if scalability is key, and real-time decision-making for digital plans or policy enforcement.
Expert Tip: Design the architecture to support parallel environments (e.g., staging, production, regulatory sandbox) from the start so that it can save weeks during testing and launch.
Choose the Right Tech Stack
Your tech stack must meet performance, scalability, and data integrity needs. Popular backend choices include Java, .NET, or Node.js; for databases, PostgreSQL or Oracle DB are common. Consider frameworks and APIs that enable integration with telco-grade systems like Diameter, SOAP, REST, and 5G network slices.
This stage also includes evaluating cloud-native (Google cloud, AWS, Azure) or on-premise deployments and deciding whether to adopt a SaaS telecom billing solution or develop a full-fledged custom telecom billing and software solution.
Expert Tip: Build for flexibility, even if you’re starting with postpaid billing, your stack should be able to support real-time prepaid or hybrid use cases later.
Core Functionalities Development
Now comes the actual development of functional modules based on the finalized architecture. Develop each module based on the required features, such as usage collection, rating engine, billing scheduler, invoice generator, payment processor, tax engine, reporting dashboard, and audit logging.
Use agile sprints to develop and validate each module independently.
Expert Tip: Make each module testable in isolation with mock data pipelines. This will speed up development and avoid downstream debugging later.
Integration with External Systems
Telecom billing systems do not operate in isolation. They must integrate seamlessly with various external systems, such as CRM, ERP, tax engines, and payment processors.
Identify all third-party and internal systems your billing platform must integrate with, like CRM, OSS/BSS, ERP, payment gateways, taxation services, fraud detection tools, and KYC verification.
Bonus Read: Blockchain technology for KYC
Build retry logic, error handling, and queue-based buffering to prevent system failures during data spikes.
Expert Tip: Use an API gateway and standardize your internal APIs, as it centralizes authentication, rate limiting, and faster onboarding of partners or services.
Testing and QA
The software must be tested across multiple dimensions.
- Functional testing ensures accuracy in rate calculation, tax application, invoice creation, and payment logs.
- Performance testing checks the system’s ability to handle millions of daily transactions.
- Regulatory testing ensures full adherence to telecom compliance laws, such as GDPR, CDR retention, or TRAI/TRS guidelines.
Your QA should Include testing for concurrency (can it handle thousands of users billing at once?), fallback handling (how does it respond to payment gateway failures or system errors?), and edge cases like refunds, roaming, or failed payments or follow (how refunds, roaming charges, or service suspensions are handled).
Expert Tip: Adapt proven software testing strategies and AI-powered QA solutions in this phase, especially if the billing interface includes mobile apps or portals.
Deployment
Deployment depends on whether you’ve opted for a SaaS, cloud-native, or on-premise billing solution. Cloud deployments offer flexibility, autoscaling, and resilience, while on-premises give you full control in highly regulated regions.
Set up load balancers, failover clusters, monitoring tools, and backup strategies. You’ll also need strong encryption protocols and tokenization for payment and personal data security.
Set up multi-zone or multi-region deployments to ensure disaster recovery and load balancing. Ensure encryption at rest and in transit using TLS 1.2+ and AES standards.
Expert Tip: Plan for continuous deployment. Implement CI/CD pipelines for automated deployment and testing of new features, making it easy to launch updates and fixes in real-time.
Training and Documentation
After deployment, internal teams need training and clear documentation to maximize the system’s effectiveness.
Once the system is stable, train billing operations teams, support agents, and finance admins to use the platform, troubleshoot errors, and manage invoices or payments.
Create SOPs for key workflows like billing, invoice re-generation, tariff updates, and dispute handling. Documentation should include user manuals, developer guides, API references, error codes, and escalation paths.
Expert Tip: Involve real end-users during training; they’ll surface usability issues you might’ve missed during UAT.
Post-Deployment Support and Maintenance
This is the final step, ensuring that the system continues functioning smoothly and adapts to any changes. The system must be actively monitored, including bug fixing, SLA-based support, performance tuning, feature launches (like adding eSIM support or IoT bundles), and staying compliant with evolving regulations.
Set alerts for abnormal usage patterns, payment failures, or tax mismatches. Run monthly reconciliation scripts and usage audits. Keep the DevOps team on retainer to release quick fixes and respond to compliance changes.
Expert Tip: Create a feedback loop in which customer support tickets and operational logs inform future product improvements. This will help evolve your billing software continuously.
Data Migration
This step is optional. If replacing an old system, you will need a secure and structured cloud data migration strategies and process. This involves securely transferring all historical and live data, such as customer profiles, usage records, payment history, KYC details, active plans, and billing cycles, into the new telecom billing system without any data loss, corruption, or duplication.
Expert Tip: Run both systems in parallel for a month in a shadow mode to compare billing outputs and catch any mismatches early.
How Much Does it Cost to Build Telecom Billing Software?
Everything from the features you need and the platforms you plan to support, to the level of automation, security, and long-term maintenance, determines the final cost of your telecom billing software. The telecom billing software development cost typically ranges between $45,000 and $350,000 or more, depending on various factors. Let’s examine the cost in detail:
Cost Analysis Based on Software Features and Functionalities
- Basic Features ($45,000–$100,000): Includes essentials like customer account management, usage tracking, invoice generation, payment processing, and simple reporting dashboards. Ideal for MVPs or telecom startups.
- Advanced Features ($150,000–$250,000): Adds multi-currency billing, complex tariff management, configurable workflows, partner settlement, and third-party system integrations.
- AI & Automation Features ($300,000+): Incorporates AI-driven modules like predictive billing analytics, intelligent dunning systems, or automated customer support bots. Best suited for enterprises looking to scale operations with automation.
Cost Analysis Based on UI/UX Design Complexity
- Simple UI/UX ($5,000–$15,000): Basic layout with minimal branding, limited customization, and essential responsive design for web and mobile.
- Advanced UI/UX ($20,000–$50,000): Custom dashboards, animations, data visualization components, multilingual support, dark/light modes, and detailed user flows tested for different user roles (e.g., billing admins, CSRs, customers).
Cost Analysis Based on Technology Stack and Platform
- Single Platform ($45,000–$150,000): Web-based platform with APIs and backend systems built using Java, Node.js, PostgreSQL, etc.
- Multi-Platform ($200,000+): Web, Android, and iOS interfaces, built with tech stacks like Flutter, React Native, or platform-specific native languages. This also includes responsive design for tablets, operator dashboards, and mobile billing apps.
Cost Analysis Based on Integration with Third-Party Systems
- Standard Integrations ($10,000–$30,000): Covers plug-and-play integration with popular systems like payment gateways (Stripe, PayPal), CRMs (Salesforce, Zoho), and SMS/email gateways (Twilio).
- Custom Integrations ($50,000+): It involves deep integration with existing OSS/BSS systems, interfacing with telecom network elements for real-time CDR capture, regulatory databases, proprietary ERP integration, and integration with government KYC APIs.
Cost Analysis Based on Compliance and Security
- Basic Compliance ($5,000–$15,000): It includes GDPR adherence, simple audit trails, basic role-based access control, and SSL encryption.
- Advanced Security & Compliance ($20,000–$50,000+): It includes end-to-end encryption, PCI-DSS compliance for payment processing, multi-factor authentication (MFA), real-time alerting and logging systems, and country-specific telecom compliance like TRAI (India), FCC (USA), or GDPR (EU).
Cost Analysis Based on Maintenance and Support
Annual Maintenance: Software maintenance cost typically ranges 15%–20% of the original development cost. It covers bug fixes and patch management, regulatory updates (e.g., tax changes or compliance adjustments), system performance monitoring, and ongoing feature upgrades or user-requested customizations.
Note: These estimates are indicative and can vary significantly based on your specific business requirements, feature scope, and technical architecture.
Quick Formula to Estimate Telecom Billing Software Development Cost
Total Cost = (Development Hours × Hourly Rate) + Cost of Cloud/API Infrastructure + Licensing/Compliance Overheads
Example: 1,500 hours × $70/hour = $105,000
Note: Hourly rates vary by team location and expertise in telecom architecture (e.g., OSS/BSS, 5G, CRM integrations).
Development Timeline: How Long Does It Take?
Telecom billing solutions generally take 9–15 months to develop. Here’s a typical timeline breakdown:
- Discovery & Planning (3–4 weeks): Define revenue model, billing types (prepaid/postpaid/hybrid), and integrations.
- UI/UX Design (4–6 weeks): Design self-care portals, invoicing interfaces, and admin dashboards.
- Development (12–24 weeks): Build modules for mediation, rating, charging, invoicing, and payment collection.
- Testing & QA (4–6 weeks): Load testing, billing accuracy checks, and interconnect settlement validations.
- Deployment (2–3 weeks): Launch on cloud (e.g., AWS, Azure), enable data encryption, and configure failover systems.
- Post-launch Support: Ongoing SLA monitoring, dispute resolution, and dynamic tariff updates.
Expert Tip: Consider launching a pilot version for internal teams or regional users first. It helps validate real-world billing accuracy and user flows before a full-scale launch.
Key Factors Influencing Telecom Billing Software Costs
Telecom billing software development involves several technical and strategic decisions that directly influence the overall cost. Here’s a detailed breakdown of major cost influencers:

UI/UX Design Complexity
A telecom billing platform serves multiple user roles: customers, support staff, finance teams, and administrators. The more intuitive, branded, and role-specific the interface, the higher the design complexity and cost.
| Aspects |
Description |
Examples |
Cost Impact |
| Basic Design |
Standard layouts, basic flows |
Simple billing interface, manual invoice list |
Low ($5,000–$10,000) |
| Moderate Design |
Customized dashboards, responsive design |
Role-specific panels for prepaid/postpaid |
Medium ($10,000–$20,000) |
| Complex Design |
Data visualization, real-time billing charts |
Real-time usage dashboards, drag-and-drop UI |
High ($20,000–$50,000+) |
Backend Development
The backend of a telecom billing system processes large volumes of data CDRs, rating rules, charging logic, and tax calculations. Its complexity and scalability have a significant impact on cost.
| Components |
Description |
Examples |
Cost Impact |
| Basic Backend |
Manual input, basic data processing |
CSV-based rating sheets, manual adjustments |
Low ($10,000–$20,000) |
| Scalable Backend |
API-based architecture, multi-tenant support |
Dynamic pricing engine, scalable CDR mediation |
Medium ($20,000–$40,000) |
| Custom Backend |
Built for automation and concurrency |
Automated dispute handling, SLA-based billing alerts |
High ($40,000–$80,000+) |
Third-Party Integrations
Telecom billing platforms typically integrate with CRM systems, payment gateways, taxation APIs, and mobile network infrastructure. Each integration adds cost depending on its scope and complexity.
| Integration Types |
Purpose |
Examples |
Cost Impact |
| Payment Gateways |
Secure billing & collections |
Razorpay, Stripe, PayPal |
$5,000–$15,000 |
| Taxation Systems |
Apply regional tax rules |
Avalara, Vertex |
$3,000–$10,000 |
| CRM Integration |
Customer lifecycle management |
Salesforce, Zoho CRM |
$10,000–$25,000 |
| Network APIs |
Sync with telco infrastructure |
Diameter/SS7 protocol integrations |
$20,000–$50,000+ |
Platform Selection
Your platform strategy determines your reach, performance, and development cost.
| Platforms |
Description |
Examples |
Cost Impact |
| Web-Only |
Single-tenant, browser-based system |
Admin panel for billing teams |
Low ($20,000–$40,000) |
| Cross-Platform |
Shared codebase for web & mobile |
Customer self-care + support dashboard |
Medium ($30,000–$60,000) |
| Native Apps |
Separate iOS & Android development |
iOS self-care app + Android agent management |
High ($50,000–$100,000+) |
| Testing |
QA on devices, network, and edge scenarios |
Stress testing the mediation pipeline, LTE/5G simulation |
$5,000–$20,000 |
Advanced Technologies
Adding AI, ML, or blockchain can dramatically enhance billing accuracy, fraud detection, and revenue assurance, but also adds development overhead.
| Technology |
Purpose |
Examples |
Cost Impact |
| AI/ML Models |
Predictive billing, fraud detection |
Spot unusual billing patterns, such as overcharging or fraud, to help fix issues quickly. |
$15,000–$40,000 |
| Blockchain |
Ensure secure and transparent billing data |
Transparent roaming and interconnect settlement |
$20,000–$25,000 |
| Real-Time Analytics |
Records interconnect charges immutably for dispute-free settlements |
Suggests dynamic plan upgrades based on usage patterns |
$25,000–$60,000 |
| R&D |
Simulation and cost optimization models |
Rate plan testing, SLA tuning under traffic load |
$5,000–$15,000 |
Hidden Costs for Software Development
Now that you are aware of the primary costs involved in developing telecom billing software, several hidden costs can significantly impact your budget as the project progresses. We have mentioned some of them below:
Regulatory Compliance: Telecom billing solutions must comply with industry-specific regulations like GDPR, TRAI, or FCC. These requirements can lead to additional costs in data privacy management, documentation, and audits.
- Regulatory Compliance Updates: $3,000–$8,000/year
- Consultant Fees for Compliance: $100–$250/hour
System Integrations: Connecting your telecom billing software with existing infrastructure (CRM, ERP, OSS/BSS, and payment gateways) can incur additional costs.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: $5,000–$20,000
- Middleware Development for Integrations: $15,000–$50,000
Data Migration: When transitioning from legacy telecom systems, migrating large amounts of customer data to the new platform is a major cost. This often involves validation, transformation, and ensuring data integrity.
- Data Migration and Transformation: $10,000–$30,000
- Dual Running Systems (for Transition Period): $5,000–$15,000/month
Scalability Enhancements: As your customer base grows, your telecom billing software needs to scale accordingly. Ensuring that the system can handle increased transactions and user loads can incur hidden costs related to server capacity, database optimization, and microservices architecture.
- Cloud Infrastructure (AWS, Azure): $1,000–$5,000/month
- Database Optimization and Scaling: $10,000–$50,000
Post-Launch Maintenance: Post-launch maintenance is a recurring cost that includes updates, bug fixes, and security patches. Typically, this accounts for 15–25% of the total development cost annually.
- Annual Maintenance & Updates: 15–25% of the total development cost
- Bug Fixes & Emergency Patches: $2,000–$10,000/quarter
Training & Onboarding: Training your staff on the new system and providing user manuals for the telecom billing software can be an unplanned expense. This involves developing documentation and conducting training sessions for end users and administrators.
- Training & Onboarding Materials: $4,000–$15,000
- Employee Training Sessions: $2,000–$5,000/session
Strategies to Optimize the Cost of Telecom Billing Software Development
You can manage costs while delivering an effective, scalable system with the right approach. The key lies in focusing on essential features, using the right technologies, and leveraging efficient development practices. Below are some cost-optimizing strategies for your telecom billing software project:
Prioritize MVP Features Using Agile Methodology
Start with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) that includes the core billing functionalities, such as real-time usage tracking, customer account management, and automated invoicing. By using Agile methodology, you can iteratively develop and refine the MVP based on feedback from real users.
Leverage Open-Source Components
Integrate open-source tools and frameworks where possible. For example, MySQL or PostgreSQL can handle database management. Using open-source software reduces licensing costs and eliminates the need for custom development, significantly reducing the time and resources required to build these components from scratch.
Use Cloud-Based Billing Solutions
Instead of investing heavily in on-premise hardware and servers, you can opt for cloud solutions (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) that scale with your business needs. Cloud platforms provide flexible storage and computing power, allowing you to scale up as required.
Opt for Cross-Platform Development
For telecom billing software, a responsive and user-friendly interface is vital for both desktop and mobile users (e.g., telecom providers and customers). Using cross-platform technologies like React Native or Flutter can allow you to build mobile applications for both iOS and Android platforms with a single codebase.
Engage in DevOps and Automated QA Pipelines
Adopt a DevOps culture with automated testing and continuous integration (CI)/continuous deployment (CD) pipelines. This ensures that the telecom billing software is consistently tested, updated, and deployed with minimal manual intervention, enhancing development efficiency and reducing errors.
Building an efficient and scalable billing system in telecom software is no longer optional. Whether you’re a telecom startup or an established provider, having the right features for telecom billing software can drastically improve customer satisfaction, reduce revenue leakage, and streamline operations.
This Telecom Billing System Guide has covered everything from architecture to cost, offering deep insights into telecom billing and software solutions that deliver real business value. From understanding the role of the telecom charging system to evaluating the benefits of telecom billing systems, this will help you make informed, future-ready decisions. Investing in the right billing infrastructure now sets the foundation for long-term growth and adaptability in a rapidly changing industry.
Create Custom Telecom Billing Software with Appinventiv
As telecom business models evolve from ARPU to experience-led revenue, a scalable and intelligent billing system becomes indispensable. Whether you’re a telco, MVNO, or a digital-first connectivity provider, building or upgrading your telecom billing software is an investment in operational agility, monetization potential, and long-term scalability.
As a trusted telecom software development company, we specialize in building next-gen telecom billing platforms tailored for 5G, SaaS, IoT, and hybrid monetization models. With deep domain and telecom software development services expertise and cross-functional tech capabilities, we help you transform billing from a cost center into a strategic differentiator. Here’s how:
- Custom Telecom Software Development Services: We design scalable, telecom-specific billing systems tailored to your pricing models, invoicing flows, and regulatory needs.
- Deep Telecom Software Expertise: With decade of experience, we’ve built robust B2B telecom platforms handling high-volume transactions and complex workflows.
- Agile, Collaborative Delivery: We follow agile development for faster iterations, continuous feedback loops, and on-time delivery.
- Next-Gen Tech Integration: Our solutions leverage AI, IoT, blockchain, and ML to power smart billing, automation, and security.
- Proven Success at Scale: Trusted by global brands, 3,000+ projects delivered by 1,600+ tech experts across industries.
Ready to build a telecom billing system that’s smart, secure, and scalable? Contact our experts today!
FAQs
Q. What is telecom software?
A. Telecom software is a set of tools that help telecom providers manage key operations such as billing, customer management, service setup, and network monitoring.
Q. What is a telecom billing system?
A. A telecom billing system is a specialized software platform that tracks usage, calculates charges, and generates invoices for telecom services. It ensures accurate revenue management while offering transparency and convenience for both providers and customers.
Q. How does a telecom billing solution work?
A. A telecom billing solution collects usage data from network elements, processes it through a telecom charging system, applies tariffs, and generates customer invoices. It also manages payments, adjustments, and account balances—all in real time or near real time—to ensure smooth billing operations.
Q. What are the common challenges telecom billing systems face?
A. The biggest challenges telecom billing systems encounter include integrating with legacy infrastructure, handling real-time data processing, managing complex pricing models, and ensuring compliance with constantly evolving telecom regulations. Another challenge is scalability, the systems must evolve with increasing user loads and service diversification.
Q. What are the core features of telecom billing software?
A. Essential features for telecom billing software include real-time charging, automated invoicing, flexible tariff configuration, revenue assurance tools, and integration capabilities with CRM and OSS/BSS systems. These features help streamline operations and reduce errors across the billing lifecycle.
Product Development & Engineering
IT Managed & Outsourcing
Consulting Services
Data Services
Didn't find what you're looking for? Let us know your needs, and we'll tailor a solution just for you.























 Faster & Error-Free Billing
Faster & Error-Free Billing






